Microsoft Endpoint Manager assists you in protecting your organization’s digital resources. Devices, applications, and data are examples of these resources. These resources can be protected using the settings for these resources. The Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center is used to configure the settings. These settings are contained in rules that you define and apply to your organization’s devices, apps, and users. You can apply these policies to your whole organization or to certain groups. And they are either users or gadgets.
In this article we are going to learn about how to manage and safeguard your organization’s devices, apps, and data. And understand the endpoint environment and available platforms as they relate to important endpoint management considerations.
How to manage and protect devices
As part of your efforts to protect endpoints, you can develop and implement device policies. Microsoft Intune assists you in securing the devices you control as well as the data saved on those devices. Managed devices are another name for protected devices. Profiles can be created for a variety of devices and systems, including iOS/iPad OS, macOS, Android, Android Enterprise, and Windows. Then, using Intune, “assign” the profile to the devices.
There are policies for various types of devices. Device policies allow us to take a variety of steps to secure devices.
Restrict
- Reset
- Require
- Configure
- Protect
- Control
- Retire
These are policy examples for device configuration.
- Use of hardware functions on the smartphone, such as the camera or Bluetooth, should be limited.
- When users are locked out of their devices, reset their passcodes.
- Require devices to comply with your organization’s security policies, such as requiring each device to enter a PIN to get access.
- Configure applications that are compliant and noncompliant. If you install a noncompliant app, you’ll get a notification (and some platforms can actually block the install).
- Apps and the data they utilize should be protected.
- By adding an additional layer of security to devices, you can secure them based on their identity.
- Control the settings for Windows Hello for Business, an alternate sign-in option for Windows 10 and later.
- Remove data from devices and retire them.
- Configure email so that end users may access work email on their own devices without having to do any setup.
How to manage and protect apps
Microsoft Intune provides a number of tools to help you manage and secure your apps and data. Without controlling the device, Intune provides mobile application management (MAM) policies.
There are two configurations available in Intune MAM.
- The first is a combination of mobile device management (MDM) and mobile app management (MAM) . IT administrators can only manage applications using MAM and app protection policies on devices that are registered in Intune mobile device management in this setup (MDM).
- MAM without device enrollment is the second setup. MAM without device enrollment, also known as MAM-WE, allows IT managers to manage apps and app protection rules using MAM on devices that aren’t registered in Intune MDM.
App policies examples
App policies provide you the ability to modify and secure apps in a variety of ways. You can set up, protect, publish, monitor, and update applications for your organization’s devices and users using MAM policies in Intune.
- Apps can be added to devices and users, and they can be assigned to them.
- Assign applications to devices that aren’t Intune-enabled.
- Control the starting behavior of programs with app configuration policies.
- Data from a protected app should not be backed up.
- Copy and paste activities should be limited to other apps.
- To gain access to an app, you must enter a PIN.
How to manage and protect your organization’s data
You can prevent data breaches and unwanted access using Endpoint Manager.
Prevent data leaks
You can limit how users share and save data without exposing themselves to the danger of intentional or unintentional data leaks. You can configure app protection policies in Microsoft Intune to secure your company information on user-owned devices. It is not necessary to enroll the devices in the Intune service.
To protect corporate data, you can create app protection policies for Office mobile apps on Windows, iOS/iPadOS, and Android devices. These rules impose device requirements like an app-based PIN or business data encryption, as well as more complex controls like limiting how users utilize cut, copy, paste, and save-as functionality across managed and unmanaged applications. You can also remove business data remotely without asking people to enroll their devices.
Prevent unauthorized access
Office 365 documents and emails can be classified, labeled, and protected so that only authorized users have access to the information. After IT administrators or users specify the rules and conditions, the settings are handled automatically. Alternatively, the IT department can give users recommended settings to follow. Administrators and users can also withdraw access to data that has already been shared with others without the need for outside help. The purpose of this project is to keep track of who opens and modifies sensitive data, even after it leaves the company’s network.
What is endpoint environment
Microsoft Endpoint Manager is used to manage the endpoints in your company. As explained previously, endpoints are your organization’s mobile devices, desktop computers, virtual machines, embedded devices, and servers. Endpoints can include the apps that your company makes use of. Depending on where these endpoints are situated, they are controlled in different settings. Endpoint Manager from Microsoft controls a variety of endpoint scenarios, including cloud, on-premises, and co-managed endpoints.
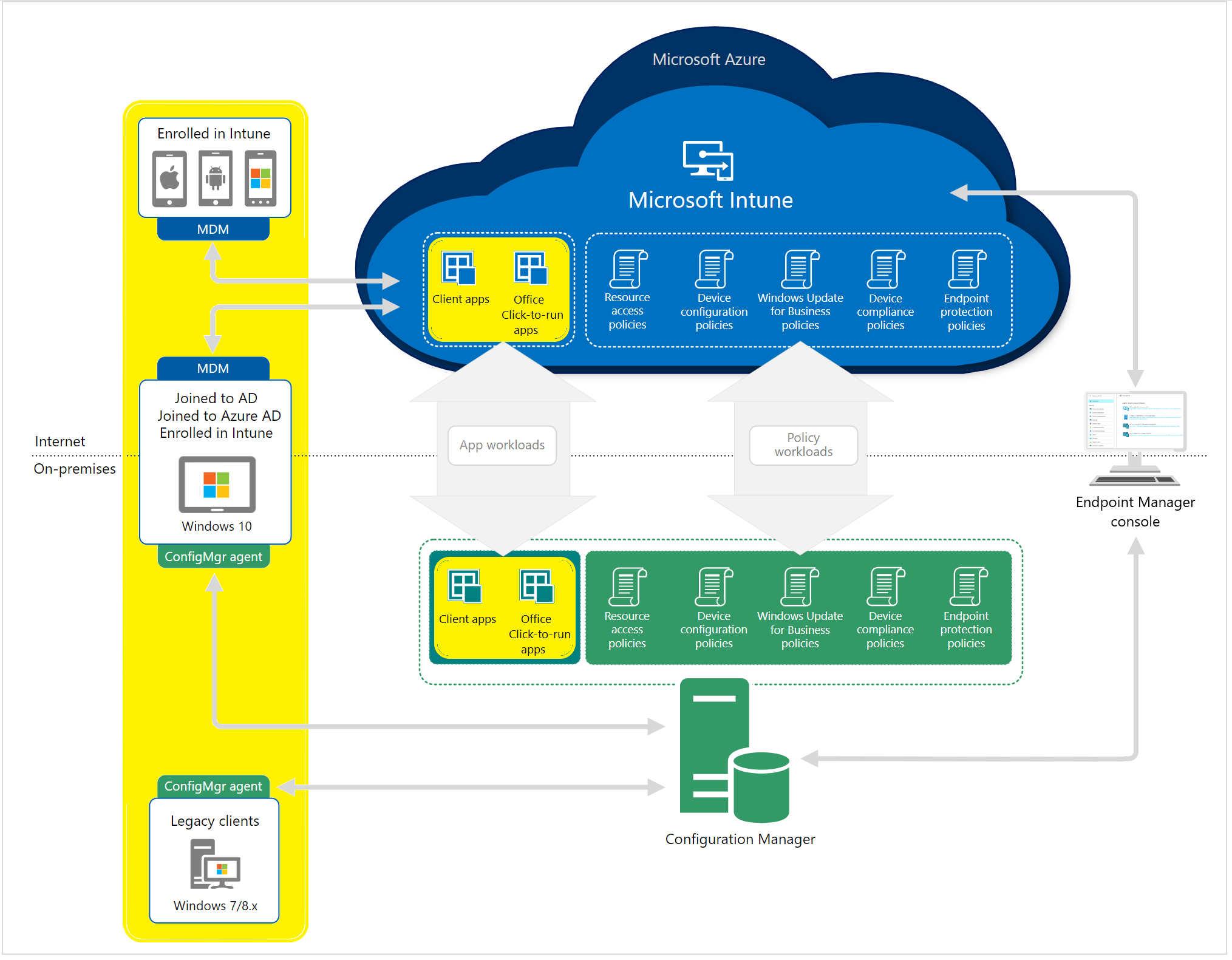
Cloud endpoint management
A cloud-based mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) solution, such as Microsoft Intune, can help you manage devices, apps, and data. To manage who has access and what they have access to, Intune interfaces with other services such as Microsoft 365 and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). Intune also works with Azure Information Protection to keep your company’s data safe. When you combine Intune with Microsoft 365, you can allow your employees to be productive across all of their devices while keeping your company’s data safe.
On-premises endpoint management
You can manage your on-premises Windows 10 devices, applications, and data, as well as optimize downloads and content, using an on-premises endpoint management solution. Your environment is more secure if you restrict access and location. Remote devices will not be able to access enterprise apps or data for your end users. Those remote devices will not be secured as corporately recognized endpoints if you simply employ an on-premises solution. If you’re using Configuration Manager, you should connect it to the Microsoft 365 cloud, which will allow you to integrate it with Intune, Azure AD, Microsoft Defender ATP, and other cloud services.
Cloud + on-premises endpoint management
The ConfigMgr connection allows data from Configuration Manager-managed devices to flow to Microsoft Endpoint Management. Tenant attach refers to the process of connecting the ConfigMgr connection to the cloud. It does not need turning on co-management and only requires a connection to an Intune tenant.
Co-managed endpoint management
Co-management is when you use Configuration Manager and Microsoft Intune to manage Windows 10 devices at the same time. By utilizing Intune and other Microsoft 365 cloud services, co-management integrates your existing on-premises Configuration Manager investment with the cloud. You get to pick whether Configuration Manager or Intune is in charge of management. You can maintain certain tasks on-premises while executing others in the cloud with Intune if you use co-management.
What is platform considerations
Microsoft Endpoint Manager works with a variety of devices. iOS/iPadOS, Windows, Android, and macOS are among the systems that Endpoint Manager can handle. Device types are a term used to describe these systems. Because each platform is unique, enrollment procedures, device settings, protection policy settings, configuration policy settings, custom policy settings, and remote actions are all somewhat different.
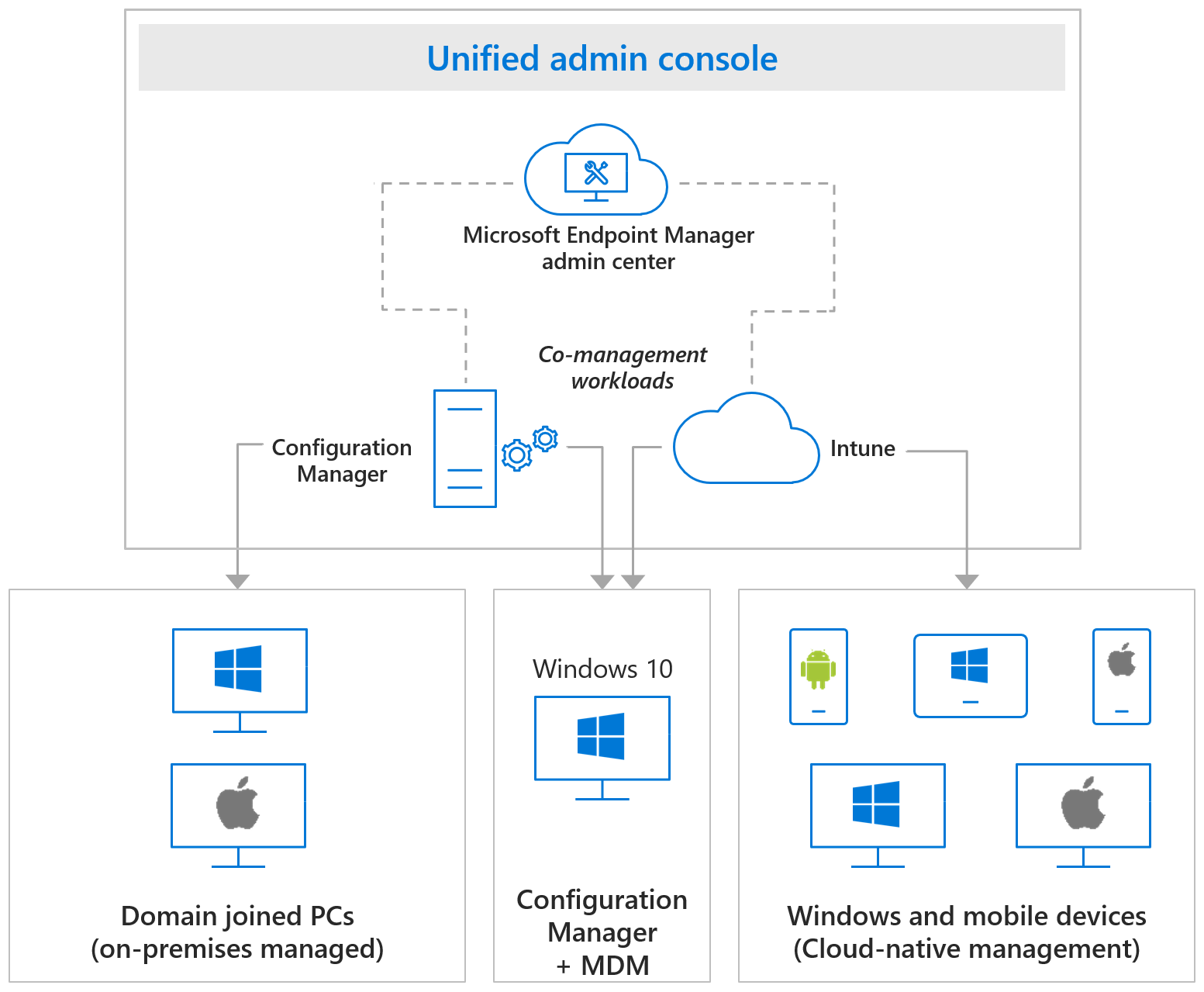
You must decide which systems in your endpoint environment must be supported. When you’ve decided which platforms you’ll need to support, you’ll need to check whether each one is supported by Intune when creating your endpoint management design.
Intune supported operating systems
Apple
- Apple iOS 11.0 and later
- Apple iPadOS 13.0 and later
- macOS X 10.12 and later
- Android 5.0 and later (including Samsung KNOX Standard 2.4 and higher)
- Android Enterprise
Microsoft
- Surface Hub
- Windows 10 (Home, S, Pro, Education, and Enterprise versions)
- Windows 10 Enterprise 2019 LTSC
- Windows 10 Mobile
- Windows 10 IoT Enterprise (x86, x64)
- Windows 10 IoT Mobile Enterprise
- Windows Holographic for Business
Several dozen operating systems are available for clients and devices that may be controlled by Configuration Manager. The following is a list of operating systems and device types in general:
- Windows computers
- Windows 10 (x86, x64, ARM64): Enterprise, Pro, Education, Pro Education, Pro for Workstation, Windows Insider
- Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB, Enterprise 2016 LTSB, and Enterprise LTSC 2019
- Windows 8.1 (x86, x64): Professional, Enterprise
- Windows Servers (several variations available)
- Windows Server Core (several variations available)
- Azure Virtual Desktop
- Windows Embedded computers (several variations available)
- Windows 10 IoT Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Team for Surface Hub
- Mac computers (several variations available)
You’ve learnt how to use Microsoft Endpoint Manager to secure your endpoint environment in this article. Here are a few of the topics you learned:
- The Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center is where you customize the settings that are then applied to your organization’s devices, applications, and users.
- Policies that you establish include the settings that you assign.
- You create groups and set policies to them.
- As part of your endpoint security initiatives, you can establish and deploy device policies.
- Whether you enroll the device or not, Intune mobile application management (MAM) functions are supported.
- You can prevent data breaches and unwanted access using Endpoint Manager.
- Cloud endpoints, on-premises endpoints, cloud Plus on-premises endpoints, and co-management endpoints are all included in endpoint management.
- The types of devices and operating systems that are supported are referred to as platforms. Apple, Google, and Microsoft platforms are all supported by Intune.










